
At the European University Institute Climate Week organised by the School of Transnational Governance in Florence on 6-8 May 2025, Robert Jeszke, Head of The National Centre for Emissions Management (KOBiZE), was a speaker at the session „Twenty years of EUETS: looking back, looking Ahead” on the best experiences and lessons learned on the EU ETS.
It was a great opportunity to exchange views and deepen understanding of the evolving EU ETS. Also in attendance were Peter Vis, Michael Pahle, Ingvild Sørhus, Beatriz Yordi and Antoine Dechezleprêtre.
In his intervention, Robert stressed that the EU ETS has proven to be an effective and credible tool for reducing emissions and remains a cornerstone of EU climatepolicy. However, the system is evolving over time – and as we approach the so-called “end game”, when EUA allowances are expected to run out around 2040, the nature of the system will inevitably change.
To remain a strong pillar of EU climate policy, the EU ETS needs to adapt and become more flexible. This includes the integration of carbon removals – both technological (such as DACCS & BECCS) and natural (AFOLU) – which are essential to achieve climate neutrality. Expanding cooperation with other carbon pricing systems – including alignment with neighbouring countries through mechanisms such as Article 6 of the Paris Agreement – and allowing the use of high-quality international offsets can help increase market liquidity, reduce compliance costs and raise global ambition.
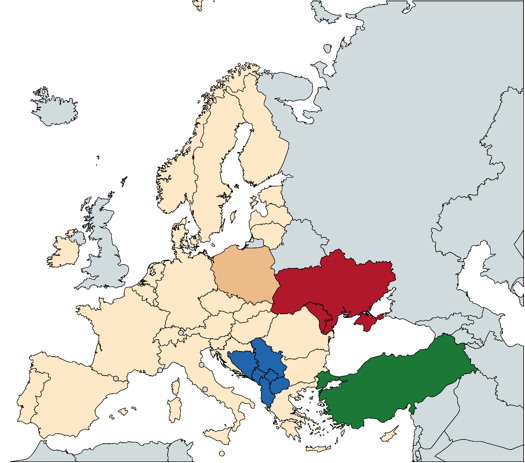
Robert highlighted that this is exactly what we are working on at CAKE as part of the LIFE ENSPIRE project – we are exploring the potential benefits, challenges, and emission reduction impacts of integrating selected EU neighbouring countries (such as Balkans, Moldova, Ukraine and Turkey) into the EU ETS, and assessing how their inclusion could affect the overall effectiveness of the system.
Finally, he pointed out the growing need for structured governance. A dedicated institution such as a European Central Carbon Bank (ECCB) could play a key role in managing removals, offsets and market stability in a more complex future EU ETS.
Project: “ENSPIRE: Exploring New Scenarios for the Progressive Integration of Neighbouring States into the EU ETS”
Authors: CAKE/KOBiZE/IOS-PIB, Poland
During the implementation of the LIFE Climate CAKE PL and LIFE VIIEW 2050 projects one of the major actions is to develop modelling tools to help gather and analyse the data on energy-climate policy. As a result, 4 new models (CGE, energy, transport, agriculture) are available and provide essential input for policymakers in the decision-making process. Therefore, to enhance our actions, based on our own well-functioning modelling tools the next reasonable move would be to develop analyses to support discussions on extending EU ETS areas.
|
Project
|

LIFE ENSPIRE
“Exploring New Scenarios for the Progressive Integration of Neighbouring States into the EU ETS beyond 2050”
|
|
Duration
|
01.10.2024 – 31.10.2028
|
|
Target audience
|
European Commission, government and state administration of the Member States, neighbouring countries and Polish central administration
|
|
Brief description
|
- The LIFE ENSPIRE project aims to assess the potential impacts of the evolving European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) and Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) on the EU and selected neighbouring countries.
- LIFE ENSPIRE will develop an analytical framework, including datasets and numerical models, designed to examine the impact of climate policies in the EU and in the neighbouring regions on emissions and economic growth paths, taking into account trade interdependencies and differentiated mitigation options.
- It aims to identify and address challenges related to achieving net-zero emissions by these countries in convergence with the EU.
- By establishing broader and more robust international networks of experts, LIFE ENSPIRE aims to enhance global cooperation in climate policy-making.
|
|
Area of interest in
the context of EU ETS
|
Inclusion in the EU ETS of other countries bordering the EU:
- Analyzing the potential benefits and challenges of integrating selected EU neighbouring countries into the EU ETS;
- Assessing the impact of including these close-border EU states on emission reduction efforts and overall effectiveness of the EU ETS;
Impact of border connected matters on EU ETS functioning:
- Investigating the influence of energy transmission from selected EU neighbouring countries on the functioning of the EU ETS;
- Assessing the implications of trade of goods, specifically Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), on the EU ETS and its market dynamics;
Extension the calculation horizon beyond 2050:
- Analysing the impact of longer calculation horizons on emissions reduction targets, carbon pricing mechanisms, and investment strategies.
|
|
Objectives
|
- Developing and providing a high-quality accessible information and data.
- Raising the environmental awareness of the public (including outside EU) through wide dissemination of high-quality information and data.
- Building broader and stronger international networks of experts (including outside EU).
- Extending and applying the sectoral and macroeconomic models.
|
|
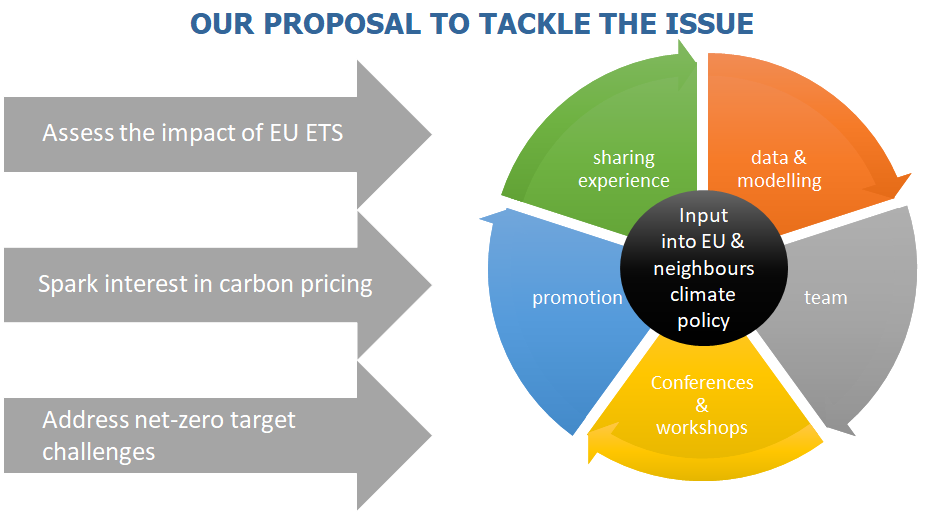
Actions
|
Analytical work
The analytical part of the project will be to identify policy instruments, acquire data, extend the available models and develop analyses on the above mentioned topics.
Dissemination – Stakeholder involvement
The effects of the analytical work will be shared in publications, during workshops, seminars, conferences and within the platform of international experts.
Transferability and replication
We will undertake intensive cooperation with the target group, including the European Commission and government administration, so that the results of our work can be used in the design of a policy framework.
|
The CAKE team has a range of analytical tools at its disposal, which have been developed in previous LIFE projects. These include the d-Place general equilibrium model (at a global scale) and the sectoral models operating at an EU scale (i.e. the energy (MEESA), transport (TR3E) and agriculture (EPICA) models). The following brief descriptions are provided for each model:
- The d-Place model is a recursive, dynamic, multi-sectoral Computed General Equilibrium (CGE) model with global coverage, based on current GTAP data. The model differentiates between 20 industries/commodities and 19 regions, including 9 EU and 10 non-EU regions. The model operates within a 5-year timeframe, with a projected time horizon of the year 2050. From a methodological perspective, the d-Place model is founded on conventional Computable General Equilibrium (CGE) formulations, incorporating nested Leontief-CES production functions, marginal cost pricing, and trade that is based on Armington assumptions. The model implements the EU ETS with emission reduction targets, as well as technical options for emission reductions and energy efficiency improvements, thus rendering it an excellent tool for analysing different climate policy strategies.
- The MEESA model is a linear energy optimisation model that currently covers EU countries, in addition to the United Kingdom, Norway and Switzerland. The model under consideration encompasses approximately 50 energy technologies, including conventional units, renewable energy sources (RES), bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS), carbon capture and storage (CCS), green hydrogen units, and energy storage (batteries, hydrogen, pumped storage). The model employs an annual disaggregation of demand into characteristic days for different seasons, with the allocation of demand occurring within 2-hour time slots. The model also considers the electricity demand for BEVs and its impact on the energy system.
- TR3E is a partial equilibrium model that is based on a bottom-up approach. The transport model incorporates the four primary transport modes (road, rail, air and water) for the conveyance of passengers and freight, along with a maximum of 37 additional transport modes. It also encompasses the characteristics of various engine types and the technology options available for each mode. TR3E encompasses all 28 countries (EU + UK), and is resolved with a time horizon extending up to 2050 within an annual timeframe.
- EPICA can be defined as an optimisation model. The scope of the study encompasses the 27 EU member states and the UK. The structure of the agricultural sector in each country is optimised separately. The d-Place model is employed to facilitate the iterative exchange of solutions, with the objective of ensuring market equilibrium in the agricultural sector at the EU level. In order to comprehensively assess the responses of the agricultural sector to policy actions, the optimisation module at its basic level is divided into interlinked crop and livestock production (19 activities), each represented by both extensive and intensive production intensities. The model incorporates the elements of labour, nutrients (N, P, K) and animal feed balances. The model’s output encompasses the projected supply and prices of agricultural products, as well as greenhouse gas emissions from the sector, for all countries considered under assumed climate policy scenarios.
